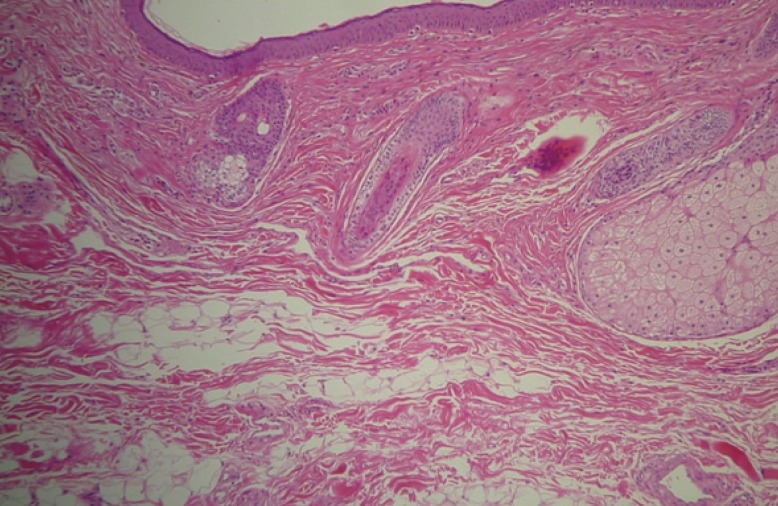
Xanthelasma palpebrarum appears as yellowish fibrotic plaques on the eyelids, resulting from the deposition of cholesterol-laden histiocytes in the dermis. Histologically, xanthelasmas are composed of xanthoma cells, or foam cells, which are typically found in the middle and superficial layers of the dermis of perivascular and periadnexal locations, with evidence of concurrent fibrosis and inflammation. In some cases, xanthelasma can infiltrate the muscle layer and muscle resection is required for complete excision of the lesion. Muscular infiltration is found in approximately 25% of patients. Incomplete excision of the lesion leads to a higher incidence of recurrence.
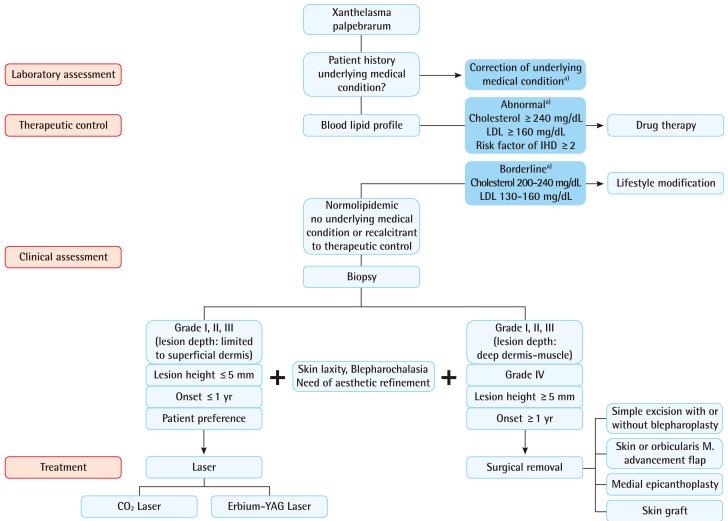
Numerous treatment options, both local and systemic, have been reviewed in the Past, including surgical excision; ablation with various lasers such as carbon dioxide, erbium-YAG, pulsed dye , and Nd-YAG; trichloroacetic acid peels; and treatment of the underlying medical condition. However, each method of treatment is associated with limitations and complications such as persistent erythema, recurrence, ectropion, scarring, and hypo- or hyperpigmentation. Mendelson and Masson found that 40% of patients had a recurrence after primary surgical excision, 60% after secondary excision, and 80% recurrence occured when all four eyelids were involved. Mendelson and Masson did not mention lesion extension in regard to depth, and they may not have acquired an adequate resection depth margin in the surgical treatment of xanthelasma palpebrarum which accounted for relatively high recurrence rate. However, this was not discussed in their paper, and it is difficult to draw any conclusions.
In some cases, treatment of the underlying medical disorder can cause regression of xanthelasma palpebrarum. Therefore, systemic treatment of the medical condition along with modified lifestyleor pharmaceutical therapy can be attempted before surgical excision or in conjunction with surgical excision. lesions on superficial area, laser therapy may suffice, but in some cases, surgery may provide a more aesthetic result. In such cases, treatment should be individualized in each case. In conclusion, among numerous treatment options for xanthelasma, we have found that for lesions involving the deep dermis and/or muscle, surgical excision is the most appropriate therapeutic option. In diffuse lesions, excision along with local flaps or skin grafting provides aesthetic reconstruction with lower recurrence