Xanthelasma palpebrarum is a skin condition that develops flat yellow growths on the eyelids. Xanthelasma is normally seen in people with high cholesterol or other fat (lipid) levels in the blood, and the lesions contain high fat (lipid-rich) deposits. Xanthelasma palpebrarum are yellowish plaques that occur most commonly near the eyelids, more frequently on the upper eyelid than the lower eyelid. Xanthelasma palpebrarum is the most common cutaneous xanthoma. There are so many treatments available “to get rid of” your xanthelasma, such as simple surgical excision, cryotherapy, chemical peeling with trichloroacetic acid, radiofrequency, and laser.
Who gets Xanthelasma Palpebrarum?
Xanthelasma can occur in any age of people and sex. However, females seem to be more frequently affected than males. In addition, it is unusual for a child or teenager to develop Xanthelasma, it mostly develops in middle age.
Approximately one-half of patients with Xanthelasma have high amounts of fats (lipids) in their blood, such as high cholesterol or high triglycerides.
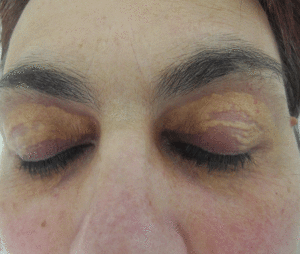
What are the Causes of Xanthelasma Palpebrarum?
- High LDL (“bad”) cholesterol or low HDL (“good”) cholesterol
- Inherited high cholesterol (your doctor might call this familial hypercholesterolemia)
- The liver disease called primary biliary cirrhosis, which can raise cholesterol levels
- It’s most common among people whose families are from Asia or the Mediterranean.
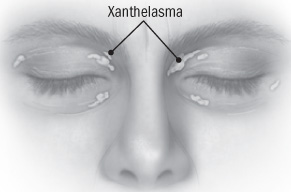
What are the Signs and Symptoms of Xanthelasma Palpebrarum?
- Presence of small, well-defined, flat skin lesions in the form of papules and plaques
- Several lesions may form around the eye, on the upper and lower eyelids; generally, the upper eyelids are affected
- The lesions may have yellowish discoloration
- They are usually painless; some are tender to touch
- When these increase in size, they are denoted as xanthomas. Some may grow large over many months, to form tumors
- In some individuals, the lesions are observed to form symmetrically around the eyes

What are the Risk Factors ?
- you’re a woman
- you’re between the ages of 30 and 50
- you’re of Asian or Mediterranean descent
- you’re a smoker
- you’re obese
- you have high blood pressure
- you have diabetes
- your lipid levels (the fats in your blood, including cholesterol) are abnormally high

Is it Harmful? Xanthelasma is not very harmful or painful but they indicate that you have dangerously high cholesterol levels and will be at the next risk of heart disease.
In Medical term
High cholesterol level causes xanthoma, however, it may also be found in patients with traditional or low-level cholesterol. ‘What causes Xanthelasma’ is the most frequent queries raised by sufferers of such condition.
There is smart and dangerous cholesterol. While smart cholesterol refers to alpha-lipoprotein (high-density lipoprotein), dangerous cholesterol refers to is low-density lipoprotein (low-density lipoprotein). Low-density lipoprotein triggers the xanthoma. Disease and hypercholesterolemia are popularly called transmitted high cholesterol which is the opposite causes of xanthoma.